Wen Laboratory
 Epigenetics and Transcription
Epigenetics and Transcription
Alterations in epigenetic landscape, together with genetic changes, are key events in initiation, progression and drug resistance of human cancers. The Wen Laboratory’s goal is to delineate how cancer cells, particularly pediatric cancers, exploit chromatin machinery to activate oncogenic or silent tumor suppressive gene expression programs, with the long-term goal of developing therapies to target epigenomic or epigenetic regulators for cancer treatment.
One of the lab’s current research projects is to characterize the role of ENL/MLLT1 in MLL-rearranged leukemia and other pediatric cancers. MLL-rearranged leukemia is a subtype of acute leukemia caused by MLL gene translocation, which accounts for about 70 percent of pediatric leukemia cases. Their previous work has identified the YEATS domain as a novel reader of histone acetylation (Li and Wen et al, Cell 2014) and uncovered that the ENL YEATS domain is critical for the expression of essential genes for disease maintenance in MLL-rearranged leukemia (Wan and Wen et al, Nature 2017). The lab is currently characterizing the role of ENL and its YEATS domain in tumor initiation and maintenance in a broad range of pediatric leukemias. We are also working on development of small molecules targeting the YEATS domain of ENL.
The ENL YEATS domain is frequently mutated in Wilms tumor, the most common pediatric kidney cancer. Another of the lab’s project is to investigate the molecular mechanism by which the ENL mutations contribute to Wilms tumor oncogenesis.
Dr. Wen and her team also study tumor suppressor ZMYND11, an adenovirus E1A-binding protein. She has previously identified that ZMYND11 is a bona-fide histone variant H3.3-specific reader of H3K36 methylation that regulates transcription elongation (Wen et al, Nature 2014). Her lab is now generating a knockout mouse model to determine the role of ZMYND11 in tumor suppression in vivo.
Join Our Team
The laboratory of Dr. Hong Wen is seeking a highly motivated and skilled Postdoctoral Fellow to join our dynamic team. The Wen Lab employs multidisciplinary approaches to investigate epigenetic pathways in cancer, with the goal of developing innovative epigenetic therapies for cancer treatment. Applicants with experience in mouse models, epigenetics, or strong biological backgrounds with a keen interest in cancer epigenetics are especially encouraged to apply.
News & Featured Publications
Learn More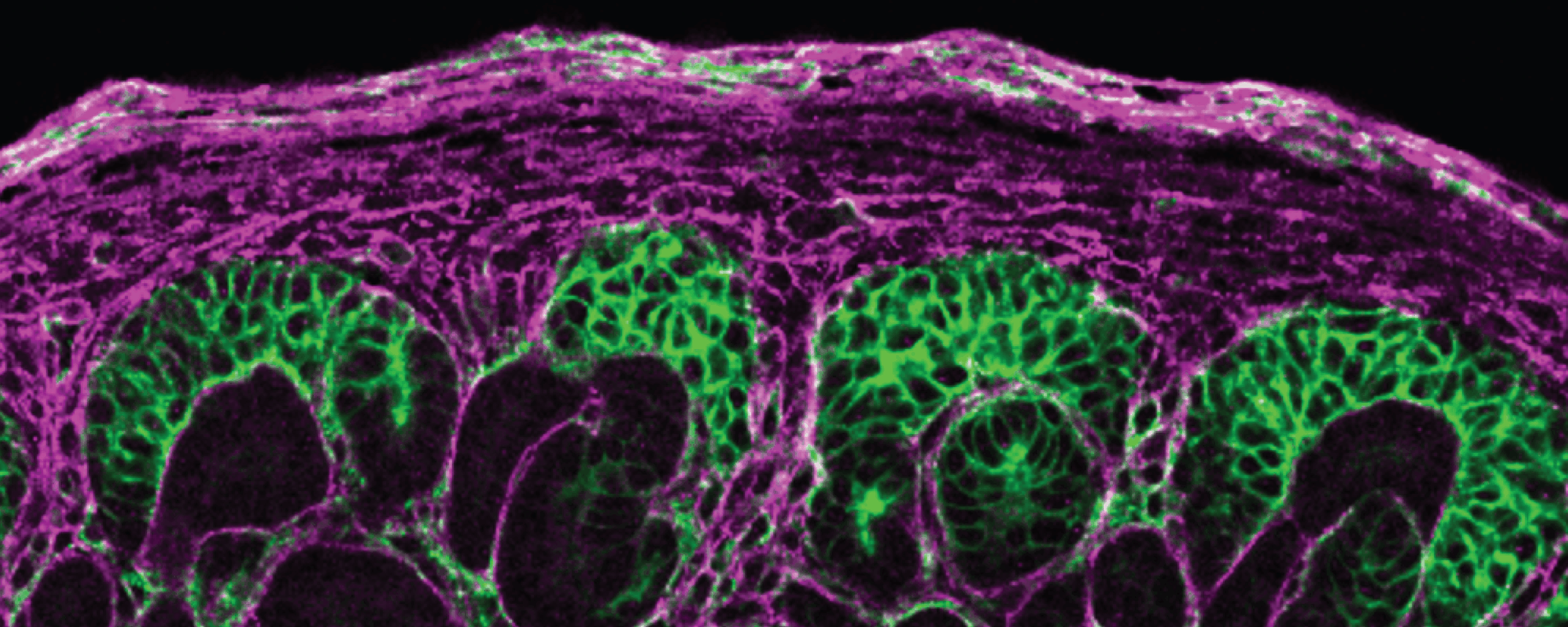
Cellular mix-ups can set the stage for kidney disease
New anti-cancer ‘degrader’ targets protein essential to infant leukemia

Engineering a lasting legacy: Prein&Newhof and Thomas and Garretta Newhof
Wan L# … Wen H#, Allis CD#. 2020. Impaired cell fate through gain-of-function mutations in a chromatin reader. Nature.
#Co-correspondence
Wan L*, Wen H*, Li Y* et al. 2017. ENL links histone acetylation to oncogenic gene expression in AML. Nature.
*Equal contribution
Li Y*, Wen H* et al. 2014. AF9 YEATS domain links histone acetylation to DOT1L-mediated H3K79 methylation. Cell.
*Equal contribution
Wen H*, #, Li Y*, Xi Y*…Li W#, Li H#, Shi X#. 2014. ZMYND11 links histone H3.3 K36 trimethylation to transcription elongation and tumor suppression. Nature.
*Equal contribution
#Co-correspondence
Our Impact
We’re raising thousands to save millions.
We’re turning hope into action for the millions of people around the world affected by diseases like cancer and Parkinson’s. Find out how you can help us make a difference.
- 141 peer-reviewed papers published in 2025, 74 of which were in high-impact journals
- 15 VAI-SU2C Epigenetics Dream Team clinical trials launched to date
- 10 clinical trials and related projects supported by VAI through the International Linked Clinical Trials Program
Hong Wen, Ph.D.
Professor, Department of Epigenetics
Areas of Expertise
Chromatin, transcription, histone modifications, epigenetics, leukemia, pediatric cancers
Biography
Dr. Hong Wen earned her B.S. in biochemistry from Wuhan University and her Ph.D. in biochemistry and molecular biology from the Shanghai Institute of Biochemistry and Cell Biology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, both with honors. She subsequently served as a postdoctoral fellow in the Department of Pathology at Stanford University. She joined the Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology at University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center as an assistant professor in 2008 and was promoted to associate professor in the Department of Epigenetics and Molecular Carcinogenesis in 2017. Dr. Wen joined Van Andel Institute in 2018 as an associate professor in the Department of Epigenetics and was promoted to professor in 2023. She is an epigenetics expert who investigates the molecular underpinnings of pediatric cancers, with a focus on how epigenetic dysregulation impacts gene expression and drives malignancy. She is also committed to developing new improved epigenetic therapies for cancer treatment. Dr. Wen is an awardee of Career Development Program Scholar from the Leukemia & Lymphoma Society.
SELECTED PUBLICATIONS
Becht DC, Selvam K, Lachance C, Côté V, Li K, Nguyen MC, Pareek A, Shi X, Wen H, Blanco MA, Côté J, Kutateladze TG. 2025. A multivalent engagement of ENL with MOZ. Nat Struct Mol Biol 32(4):709–718.
Xue Z, Xuan H, Lau K, Su Y, Wegener M, Li K, Turner L, Adams M, Shi X, Wen H. 2025. Expression of ENL YEATS domain tumor mutations in nephrogenic or stromal lineage impairs kidney development. Nat Commun 16:2531.
Xue Z*, Qin L*, Xuan H*, Luo K*, Huang M, Xie L, Su Y, Xu L, Harsh J, Dale B, Shi X, Chen X, Kaniskan JÜ, Jin J#, Wen H#. 2024. A potent and selective ENL degrader suppresses oncogenic gene expression and leukemia progression. Sci Adv 10(35).
# Co-corresponding authors
Abla O, Ries RE, Triche Jr TJ, Gerbing RB, Hirsch B, Raimondi S, Cooper TM, Farrar JE, Buteyn N, Harmon LM, Wen H, Deshpande AJ, Kolb EA, Gamis AS, Aplenc R, Alonzo T, Meshinchi S. 2024. Structural variants involving MLLT10 fusion are associated with adverse outcomes in pediatric acute myeloid leukemia. Blood Adv.
Xu L, Xuan H, He W, Zhang L, Huang M, Li K, Wen H, Xu H, Shi X. 2023. TAZ2 truncation confers overactivation of p300 and cellular vulnerability to HDAC inhibition. Nat Commun 14(1):5362.
Tencer AH, Yu Y, Causse SZ, Campbell GR, Klein BJ, Xuan H, Cartier J, Miles MA, Gaurav N, Zadoroznyj A, Holt TA, Wen H, Hawkins CJ, Spector SA, Dubrez L, Shi X, Kutateladze TG. 2023. Molecular basis for nuclear accumulation and targeting of the inhibitor of apoptosis BIRC2. Nat Struct Mol Biol 30(9):1265-1274.
Ma XR*, Xu L*, Xu S, Klein BJ, Wang H, Das S, Li K, Yang KS, Sohail S, Chapman A, Kutateladze TG, Shi X, Liu WR#, Wen H#. 2021. Discovery of selective small-molecule inhibitors for the ENL YEATS domain. J Med Chem 64(15):10997-11013.
Klein BJ, Deshpande A, Cox KL, Xuan F, Zandian M, Barbosa K, Khanal S, Tong Q, Zhang Y, Zhang P, Sinha A, Bohlander SK, Shi X, Wen H, Poirier MG, Deshpande AJ, Kutateladze TG. 2021. The role of the PZP domain of AF10 in acute leukemia driven by AF10 translocations. Nat Commun 12(1):4130.
Yu Y, Wen H, Shi X. 2021. Histone mimics: more tales to read. Biochem J 478(14):2789-2791.
Wen H, Shi X. 2020. H3.3S31 phosphorylation: linking transcription elongation to stimulation responses. Signal Transduct Target Ther 5(1):176.
Wan L#, Chong S*, Xuan F*, Liang A*, Cui X, Gates L, Carroll TS, Li Y, Feng L, Chen G, Wang SP, Ortiz WV, Saley SK, Wang X, Xuan H, Kentsis A, Muir TW, Roeder RG, Li H, Li W, Tijan R, Wen H#, Allis CD#. 2020. Impaired cell fate through gain-of-function mutations in a chromatin reader. Nature 577:121–126.
*Equal contribution
#Co-correspondence
Mi W, Zhang Y, Lyu J, Wang X, Tong Q, Peng D, Xue Y, Tencer AH, Wen H, Li W, Kutateladze TG, Shi X. 2018. The ZZ-type zinc finger of ZZZ3 modulates the ATAC complex-mediated histone acetylation and gene activation. Nat Commun 9(1):3759.
Zhang Y, Xue Y, Shi J, Ahn J, Mi W, Ali M, Wang X, Klein BJ, Wen H, Li W, Shi X, Kutateladze TG. 2018. The ZZ domain of p300 mediates specificity of the adjacent HAT domain for histone H3.
Nat Struct Mol Biol 25(9):841-849.
Shi L*, Shi J*, X S, Li W, Wen H. 2018. Histone H3.3 G34 mutations alter histone H3K36 and H3K27 methylation in cis. J Mol Biol. pii:S0022-2836(18)30248-1.
Hsu C, Shi J, Yuan C, Zhao D, Jiang S, Lyu J, Wang X, Li H, Wen H, Li W, Shi X. 2018. Recognition of histone acetylation by the GAS41 YEATS domain promotes H2A.Z deposition in non-small cell lung cancer. Genes Dev 32(1):58–69.
Wan L*, Wen H*, Li Y*, Lyu J, Xi Y, Hoshii T, Joseph J, Wang X, Loh Y, Souza AL, Bradner JE, Shen L, Li W, Li H, Allis CD, Armstrong SA, Shi X. 2017. ENL links histone acetylation to oncogenic gene expression in AML. Nature 543(7644):265–269.
*Equal contribution
Mi W, Guan H, Lyu J, Zhao D, Xi Y, Jiang S, Andrews FH, Wang X, Gagea M, Wen H, Tora L, Dent SYR, Kutateladze TG, Li W, Li H, Shi X. 2017. YEATS2 links histone acetylation to tumorigenesis of non-small cell lung cancer. Nat Commun 8(1):1088.
Shi L, Wen H, Shi X. 2016. The histone variant H3.3 in transcriptional regulation and human disease. J Mol Biol 429(13):1934–1945.
Li N, Li Y, Lv J, Zheng X, Wen H, Shen H, Zhu G, Chen TY, Dhar SS, Kan PY, Wang Z, Shiekhattar R, Shi X, Lan F, Chen K, Li W, Li H, Lee MG. 2016. ZMYND8 reads the dual histone mark H3K4me1-H3K14ac to antagonize the expression of metastasis-linked genes. Mol Cell 63(3):470–484.
Zhang X, Peng D, Xi Y, Yuan C, Sagum CA, Klein BJ, Tanaka K, Wen H, Kutateladze TG, Li W, Bedford MT, Shi X. 2016. G9a-mediated methylation of ERα links the PHF20/MOF histone acetyltransferase complex to hormonal gene expression. Nature Commun 7:10810.
Zhao D, Guan H, Zhao S, Mi W, Wen H, Li Y, Zhao Y, Allis CD, Shi X, Li H. 2016. YEATS2 is a selective histone crotonylation reader. Cell Res 26(5):629–632.
Li Y*, Wen H*, Xi Y, Tanaka K, Wang H, Peng D, Ren Y, Jin Q, Dent SR, Li W, Li H, Shi X. 2014. AF9 YEATS domain links histone acetylation to DOT1L-mediated H3K79 methylation. Cell 159(3):558–571.
*Equal contribution
Wen H*, #, Li Y*, Xi Y*, Jiang S, Stratton S, Peng D, Tanaka K, Ren Y, Xia Z, Wu J, Li B, Barton MC, Li W#, Li H#, Shi X#. 2014. ZMYND11 links histone H3.3 K36 trimethylation to transcription elongation and tumor suppression. Nature 508(7495):263–268.
*Equal contribution
#Co-correspondence
Guo R, Zheng L, Park JW, Lv R, Chen H, Jiao F, Xu W, Mu S, Wen H, Qiu J, Wang Z, Yang P, Wu F, Hui J, Fu X, Shi X, Shi YG, Xing Y, Lan F, Shi Y. 2014. BS69/ZMYND11 reads and connects histone H3.3 lysine 36 trimethylation-decorated chromatin to regulated pre-mRNA processing. Mol Cell 56(2):298–310.
Klein BJ, Piao L, Xi Y, Rincon-Arano H, Rothbart SB, Peng D, Wen H, Larson C, Zheng X, Cortazar M, Peña PV, Mangan A, Bentley DL, Strahl BD, Groudine M, Li W, Shi X and Kutateladze T. 2014. The histone-H3K4-specific demethylase KDM5B binds to its substrate and product through distinct PHD fingers. Cell Rep 6(2):325–335.
Wen H, Li Y, Li H, Shi X. 2014. ZMYND11: An H3.3-specific reader of H3K36me3. Cell Cycle 13(14):2153–2154.
Zhang X, Tanaka K, Yan J, Li J, Peng D, Jiang Y, Yang Z, Barton MC, Wen H, Shi X. 2013. Regulation of estrogen receptor α by histone methyltransferase SMYD2-mediated protein methylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110(43):17284–17289.
DeBruhl H, Wen H, Lipsick JS. 2013. The complex containing Drosophila Myb and RB/E2F2 regulates cytokinesis in a histone H2Av-dependent manner. Mol Cell Biol 33(9):1809–1818.
Andrejka L*, Wen H*, Ashton J, Grant M, Iori K, Wang A, Manak JR, Lipsick JS. 2011. An animal-specific C-terminal domain links Myb to the ancient MuvB repressor complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108(42):17438–17443.
*Equal contribution
Wen H*, Li J*, Song T*, Lu M, Kan PY, Lee MG, Sha B, Shi X. 2010. Recognition of histone H3K4 trimethylation by the PHD finger of PHF2 modulates histone demethylation. J Biol Chem 285(13):9322–9926. *Equal contribution
Wen H, Andrejka L, Ashton J, Karess R, Lipsick JS. 2008. Epigenetic regulation of gene expression by Drosophila Myb and E2F2-RBF via the Myb- MuvB/dREAM complex. Genes Dev 22:601–614.
Shi X, Kachirskaia I, Yamaguchi H, West LE, Wen H, Wang EW, Dutta S, Appella E, Gozani O. 2007. Modulation of p53 function by SET8-mediated methylation at lysine 382. Mol Cell 27(4):636–646.
Manak JR, Wen H, Van T, Andrejka L, Lipsick JS. 2007. Loss of Drosophila Myb interrupts the progression of chromosome condensation. Nat Cell Biol 9:581–587.
Wang DM, Sevcikova S, Wen H, Roberts S, Lipsick JS. 2007. v-Myb represses the transcription of Ets-2. Oncogene 26:1238-1244.


Elshaimaa Ali, M.S.
Ph.D. Student, VAI Graduate School
Research Focus: Characterization of how chromatin reader SP140 regulates gene expression

Jennifer Brooks
Senior Administrative Assistant I, Department of Epigenetics


Jeff Wang
Research Technician, Department of Epigenetics

Fan Xuan, Ph.D.
Research Scientist, Department of Epigenetics
Histone reader and epigenetic modifications in cancer

Yucong Yu, Ph.D.
Research Scientist, Department of Epigenetics

